Artificial intelligence is here to stay. However, as businesses accelerate AI adoption, privacy and compliance professionals find themselves in the middle of a high-stakes game where the rules are still being written. As artificial intelligence becomes more deeply embedded in business operations, the intersection of ai and data privacy is now one of the most critical risk areas organizations must address.
Much like the rise of social media in the 2000s, AI is transforming how organizations operate. It promises efficiency, automation, and unprecedented data insights, but it also brings legal uncertainty, privacy risks, and regulatory scrutiny. The challenge? Organizations must harness AI’s potential without sacrificing data privacy, security, or trust.
Welcome to the new frontier of AI governance. AI is reshaping industries at breakneck speed, from ChatGPT and Gemini to predictive algorithms and automated decision-making. But like any uncharted territory, this frontier is both promising and perilous. Just as early explorers needed maps and compasses, organizations must establish robust governance frameworks to safely navigate AI’s evolving landscape.
This shift has intensified global discussions around data privacy and AI, particularly as AI systems rely on vast data collection and sensitive personal data.
In this article, we will explore:
- Key AI advancements and their privacy implications.
- Top AI trends and privacy challenges expected in 2026.
- How to operationalize AI governance and mitigate risks.
- Practical strategies to ensure compliance and build trust.
This serves as a roadmap to AI privacy management in 2026 for privacy and compliance professionals.
A centralized privacy management platform like TrustArc helps organizations track evolving AI regulations, assess AI-related privacy risks, and operationalize governance across global jurisdictions.
The AI revolution: What’s changing in 2026?
AI is no longer limited to generating text and images. It is now making high-stakes decisions in hiring, healthcare, law enforcement, and finance. Its impact rivals the emergence of the internet itself, but without strong governance, AI could become more of a Pandora’s box than a productivity tool.
As AI adoption accelerates, organizations are facing increasing pressure to address AI and data privacy risks tied to automated systems and large-scale data processing.
The evolution of AI in 2026 makes data privacy and AI inseparable, especially as AI systems influence civil rights, employment, and financial outcomes.
This rapid expansion brings significant privacy risks, necessitating robust governance frameworks. Without proper safeguards, data privacy and security in AI becomes increasingly difficult to maintain as AI technologies scale.
Key privacy risks:
AI hallucinations
AI models can produce outputs that appear plausible but are incorrect, leading to potential reputational damage and compliance issues. For example, in 2023, a New York lawyer filed a legal brief citing non-existent cases fabricated by ChatGPT, resulting in professional consequences. AI hallucinations heighten AI and data privacy concerns when incorrect outputs reference personal data or sensitive information. This underscores the growing need for stronger data privacy and AI oversight in automated decision-making.
Data privacy breaches
The integration of AI has correlated with an increase in data privacy incidents. According to Gartner, 40% of organizations have reported AI-related breaches. IBM further highlights that 46% of these breaches involve personally identifiable information (PII), with the global average data breach cost reaching $4.88 million in 2024. AI-driven data processing has amplified data privacy and security in AI risks, especially where personal data and biometric data are involved. Privacy breaches involving AI systems often expose organizations to regulatory penalties and loss of trust.
Regulatory crackdowns
Governments worldwide are tightening AI regulations, with landmark laws such as the EU AI Act and the Colorado AI Act coming into force. These regulations explicitly target AI and data privacy risks tied to high-risk AI systems and automated decision-making.
Third-party AI risk
Companies are increasingly using third-party AI models, raising concerns about how vendors handle data and whether they use it to train AI without consent.
These risks necessitate AI governance strategies that align with privacy regulations while ensuring AI remains an asset rather than a liability. Third-party AI significantly increases AI and data privacy concerns, particularly around data sharing and training AI systems without explicit consent.
AI and the “right to be forgotten”
AI systems trained on personal data present challenges for data deletion rights under GDPR. Privacy professionals must determine how individuals can request AI systems to “forget” their data and whether AI-generated insights qualify as personal data. This is a growing challenge in data privacy and AI, where AI-generated insights may still qualify as personal data.
AI privacy regulations to watch in 2026
The regulatory landscape for AI is evolving rapidly. New laws increasingly treat AI and data privacy as a combined compliance obligation rather than separate issues.
Organizations must align AI development with evolving data privacy and security in AI requirements across jurisdictions. Below are some of the most impactful laws privacy professionals need to prepare for:
EU AI Act (Effective 2025–2027)
- Prohibited practices: Bans AI systems posing “unacceptable risk,” such as social scoring and mass surveillance.
- High-risk AI requirements: Mandates transparency and risk assessments for high-risk AI applications, including HR recruitment and credit scoring.
- General-purpose AI compliance: Requires compliance for general-purpose AI models by August 2027.
The EU AI Act reinforces the connection between AI and data privacy, especially for high-risk AI systems processing sensitive personal data.
Learn moreColorado AI Act (Effective 2026)
This legislation formalizes expectations around data privacy and AI governance, requiring transparency and accountability from AI deployers.
- AI-specific regulatory requirements: The first U.S. state to implement AI-specific regulations, mandating disclosures from AI developers to deployers.
- Affirmative defense: Establishes an “affirmative defense” for compliance with frameworks such as the NIST Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0).
State privacy regulations
State-level enforcement continues to expand AI and data privacy concerns tied to profiling, targeted advertising, and automated decisions.
- Expanded consumer rights: Legislation like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) requires automated decision-making and profiling transparency.
Federal Trade Commission (FTC) oversight
- Active notification and consent: The FTC has warned businesses that merely updating privacy policies is insufficient—organizations must actively notify and gain consent before using personal data for AI.
As regulatory enforcement is intensifying, businesses must proactively integrate AI governance into their privacy programs.
But staying ahead of evolving AI regulations across jurisdictions isn’t just about reading headlines—it’s about having the right research engine under the hood. Explore how Nymity Research helps privacy teams monitor regulatory updates and compare global laws with confidence.
Operationalizing AI governance: How to deploy AI ethically and compliantly
Businesses should integrate AI governance into their existing privacy frameworks to mitigate emerging AI privacy risks. Operationalizing AI and data privacy requires embedding governance controls directly into AI development, deployment, and monitoring processes.
Strong data privacy and AI governance ensures innovation does not outpace compliance.
The following steps are essential:
1. Implement AI Impact Risk Assessments (AIRA)
AI Impact Risk Assessments (AIRA) are becoming a legal requirement under laws such as the Colorado AI Act. AIRAs are essential for identifying AI and data privacy concerns, including risks tied to training data, bias, and data minimization. They directly support data privacy and security in AI by documenting risk mitigation strategies.
These assessments should evaluate:
- Bias risks in training data: Assess datasets for representativeness and potential biases.
- Potential privacy violations: Identify risks related to data misuse or unauthorized access.
- Transparency and explainability: Ensure AI decision-making processes are understandable and transparent.
- Legal compliance: Align AI practices with applicable laws and regulations.
To learn more about AI Impact Risk Assessments, explore AI Governance Behind the Scenes, Emerging Practices for AI Impact Assessments.
Aim to conduct ongoing AI risk assessments, not just one-time reviews.
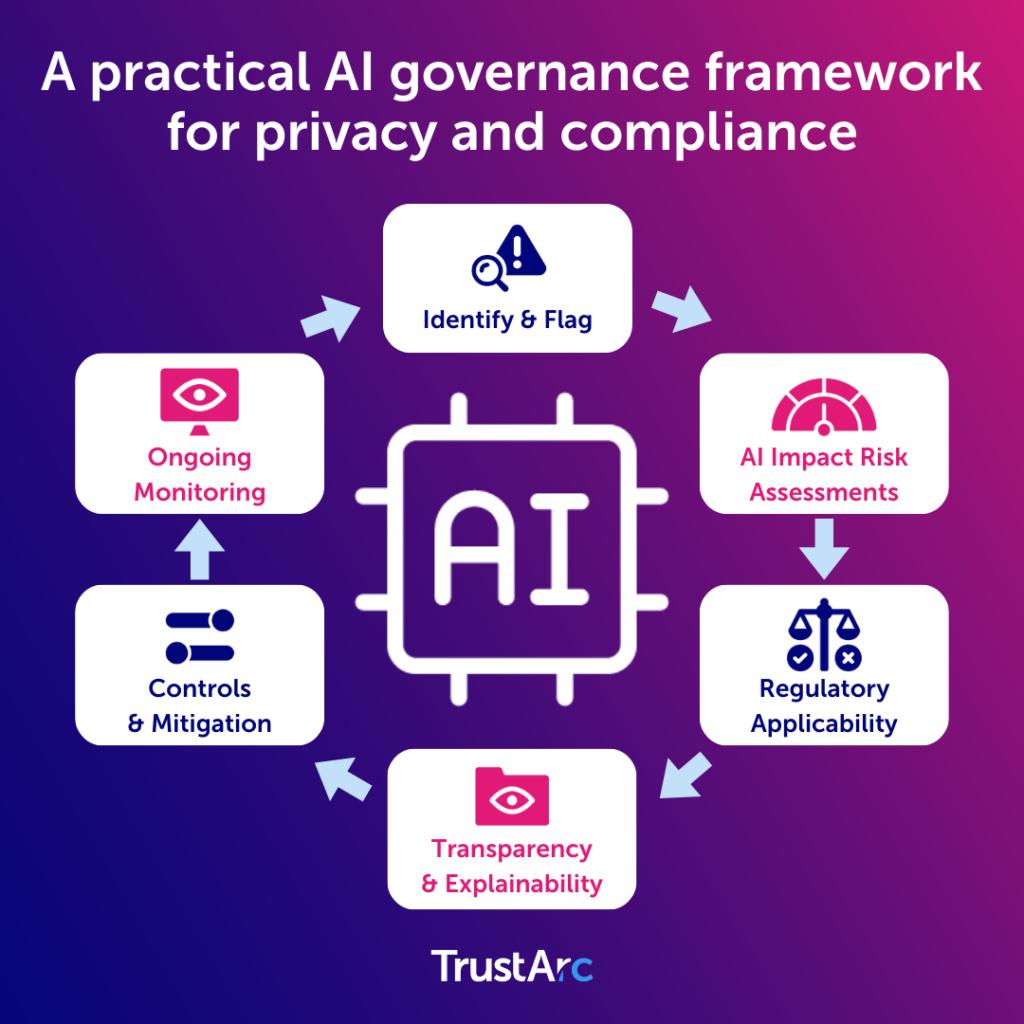
2. Establish an AI risk committee
- Cross-functional oversight: Form a committee comprising privacy, legal, compliance, and data science experts.
- Accountability: Define clear responsibilities for AI-related decisions.
- Regular reviews: Continuously assess AI model performance, ethics, and compliance.
3. Manage third-party AI risk
Third-party governance is critical to reducing data privacy and AI exposure across vendor ecosystems.
- Vendor assessments: Conduct thorough evaluations of third-party AI providers.
- Contractual safeguards: Ensure contracts prevent vendors from using company data to train AI models without explicit consent.
- Transparency clauses: Include terms requiring vendors to disclose how AI models utilize personal data.
4. Prioritize transparency and consumer rights
Transparency is a cornerstone of AI and data privacy, ensuring informed consent and trust.
- Clear disclosures: Inform consumers about AI-driven decisions, particularly in sensitive areas like hiring or lending.
- AI “nutrition labels”: Adopt standardized disclosures detailing AI system functionalities and data usage.
- Comprehensive privacy policies: Update policies to include detailed explanations of AI usage in compliance with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and the EU AI Act.
5. Monitor and mitigate AI privacy risks
- Real-time monitoring: Implement systems to detect bias, privacy violations, or inaccurate outputs.
- Manual review processes: Establish protocols for human oversight of high-risk AI decisions.
- Continuous model updates: Regularly refine AI models to align with evolving regulatory requirements.
Continuous monitoring helps organizations address evolving AI and data privacy concerns before they escalate.
Turning AI risks into a competitive advantage
AI is fundamentally reshaping industries, but its use comes with significant legal and ethical responsibilities. Organizations that proactively implement AI governance, conduct risk assessments, and prioritize transparency will gain a competitive advantage while maintaining trust with customers and regulators.
Key Takeaways
- AI regulations are tightening in 2026, with the EU AI Act and the Colorado AI Act leading the way.
- The top AI concerns are AI hallucinations, privacy breaches, and third-party risks.
- AI Impact Assessments (AIRA) are becoming essential for privacy professionals.
- AI and data privacy must be managed together through strong governance.
- Businesses must embed AI governance into their existing privacy frameworks.
- Transparency, consumer rights, and vendor risk management are critical for compliance.
Organizations that prioritize responsible AI practices will mitigate risk and build consumer trust and regulatory confidence. AI privacy risks are manageable—but only if businesses take proactive steps now.
FAQs About AI and Data Privacy
What is AI and data privacy?
AI and data privacy refers to how organizations collect, process, and protect personal data when using artificial intelligence technologies. As AI systems rely on vast amounts of training data, managing data privacy and AI together is essential to reduce privacy risks and maintain compliance.
Why are data privacy and AI closely connected?
Data privacy and AI are deeply connected because AI models often depend on personal data, sensitive information, and automated decision-making. Without strong data governance and privacy safeguards, AI technologies can increase the risk of privacy breaches and misuse of personal information.
What are the biggest AI and data privacy concerns today?
Key AI and data privacy concerns include unauthorized data collection, AI hallucinations involving personal data, privacy breaches, third-party AI risks, and lack of transparency in automated systems. These issues are especially critical in high-risk AI systems such as hiring, finance, and criminal justice.
How does data privacy and security in AI affect compliance?
Data privacy and security in AI directly impact compliance with laws like the GDPR, EU AI Act, and U.S. state privacy regulations. Organizations must implement robust security measures, data minimization practices, and transparency requirements to meet evolving legal expectations.
What role does AI governance play in protecting data privacy?
AI governance provides the structure needed to manage AI and data privacy through risk assessments, oversight committees, vendor management, and continuous monitoring. Strong governance ensures AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly while safeguarding personal data.
How can organizations reduce AI and data privacy risks?
Organizations can reduce AI and data privacy risks by limiting unnecessary data collection, protecting sensitive data, conducting AI impact risk assessments, managing third-party AI providers, and prioritizing transparency and informed consent throughout the AI lifecycle.
Privacy and AI Governance, Connected
Bring privacy, risk, and AI governance together on one unified platform. The TrustArc Platform helps teams centralize compliance, automate assessments, and stay ahead of fast-moving regulations without juggling disconnected tools.
Explore the platformAI Governance, Built for What’s Next.
Operationalize responsible AI with confidence. TrustArc’s AI Governance solution helps you assess risk, document compliance, and monitor AI systems as regulations like the EU AI Act and Colorado AI Act take shape.
Govern AI with confidence






